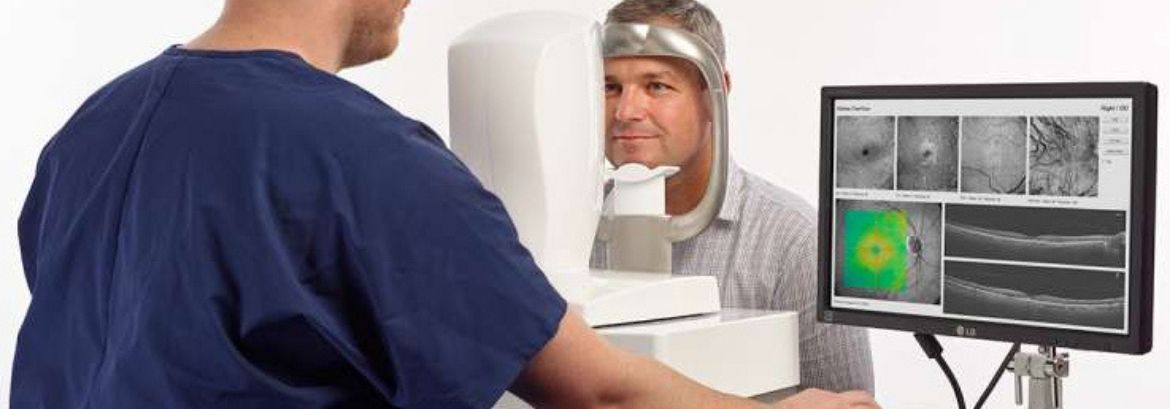
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
- OCT Macula (Diabetes Retinography)
OCT enables precise measurement of macular thickness. Thus, it facilitates detecting macular oedema which is the main pathologic feature of diabetic maculopathy. This is defined as any detectable retinal thickening due to fluid accumulation. - OCT RNFL (Glaucoma)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-contact optical technique that allows imaging and measurement of the retinal nerve fiber layer. - OCT Anterior Segment
ASOCT is useful as an adjunct to gonioscopy as well as a substitute when gonioscopy is not feasible due to cornea. In addition, it is extremely useful as a patient education tool, especially when laser peripheral iridotomy is being recommended. - Ganglion Cell Analysis
Ganglion cell analysis with optical coherence tomography provides nearly equivalent glaucoma assessment performance as conventional circumpapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement. - Angio OCT
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive diagnostic instrument used for imaging the retina. The OCT uses an array of light to rapidly scan the eye. These scans are interpreted and the OCT then presents an image of the tissue layers within the retina.
